Which Best Describes the Way Composite Volcanoes Are Built Up
Composite volcanoes also called stratovolcanoes are cone-shaped volcanoes built from many layers of lava pumice ash and tephra. Wide gently sloping mountain LAVA PLATEAUS.
4 3 Types Of Volcanoes Physical Geology 2nd Edition
Name the 5 landforms formed from lava and ash and describe their shapes.

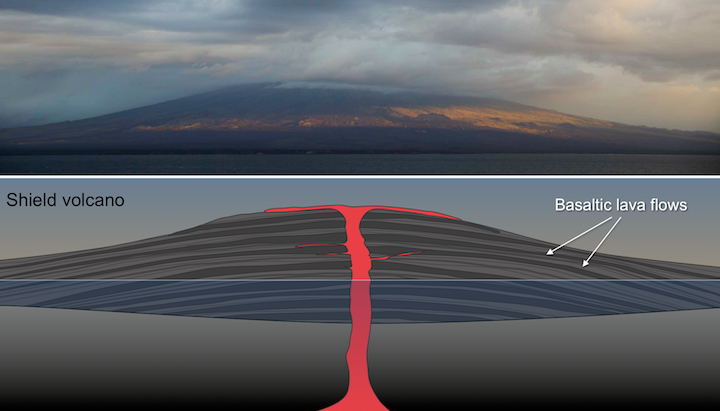
. Alternating layers of cinders and ash embedded with lava flows. Large fairly steep-sided cones composed of lavas and pyroclastic layers. Piles of basaltic lava flows built up from the ocean floor by multiple summit flank eruptions.
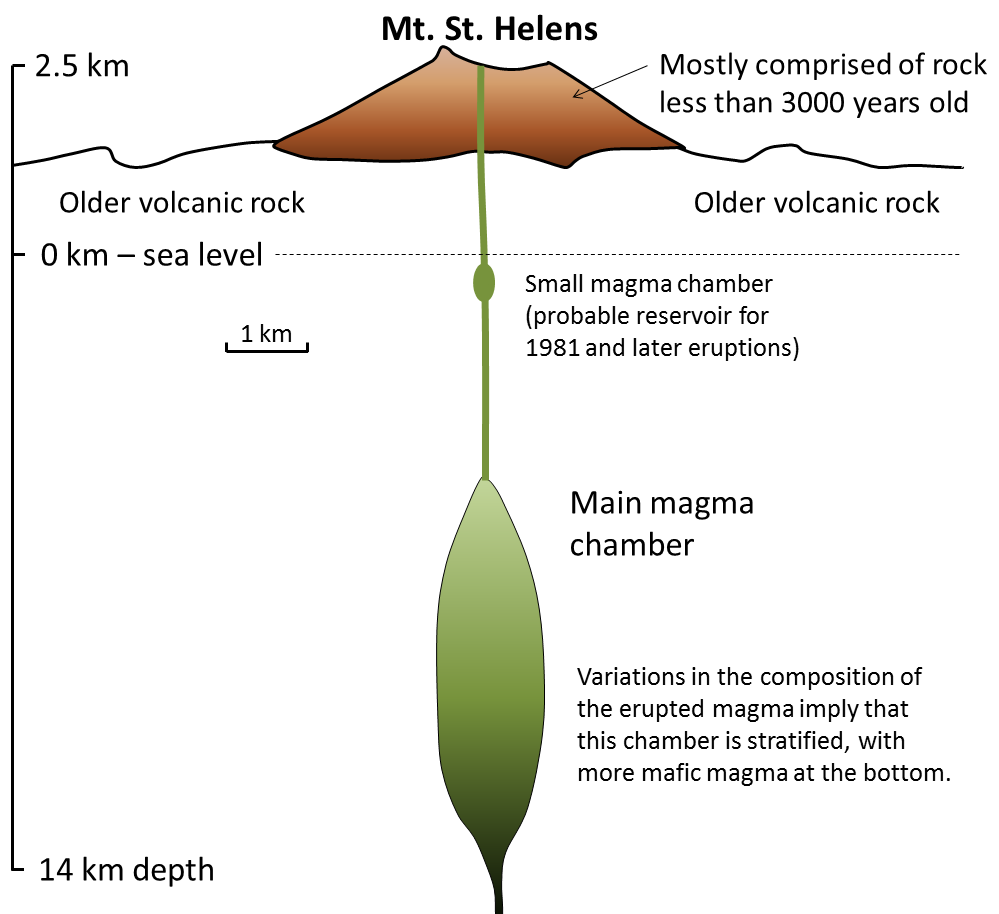
True A composite volcano also known as a stratovolcano is a tall conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava tephra pumice and volcanic ash. Dust and gas orbiting the protostar. The big volcanoes of Hawaii.
Cinder cone volcano an underwater volcano that never surfaces 6. Composite volcanoes are much more explosive than shield volcanoes the other important type of volcano because their magma contains more silica SiO2 than that of a shield volcano and is therefore stickier more viscous. A composite volcano also known as a stratovolcano is a cone-shaped volcano built from several layers of lava pumice ash and tephra.
Dike simple fold in rock layers 3. True Lava is both the molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the. The result is an explosive dangerous eruption.
Composite volcano break in rock formed from colliding plates. Strike-slip fault feature formed from rock and ash 5. Large fairly steep-sided cones composed of lavas and pyroclastic layers.
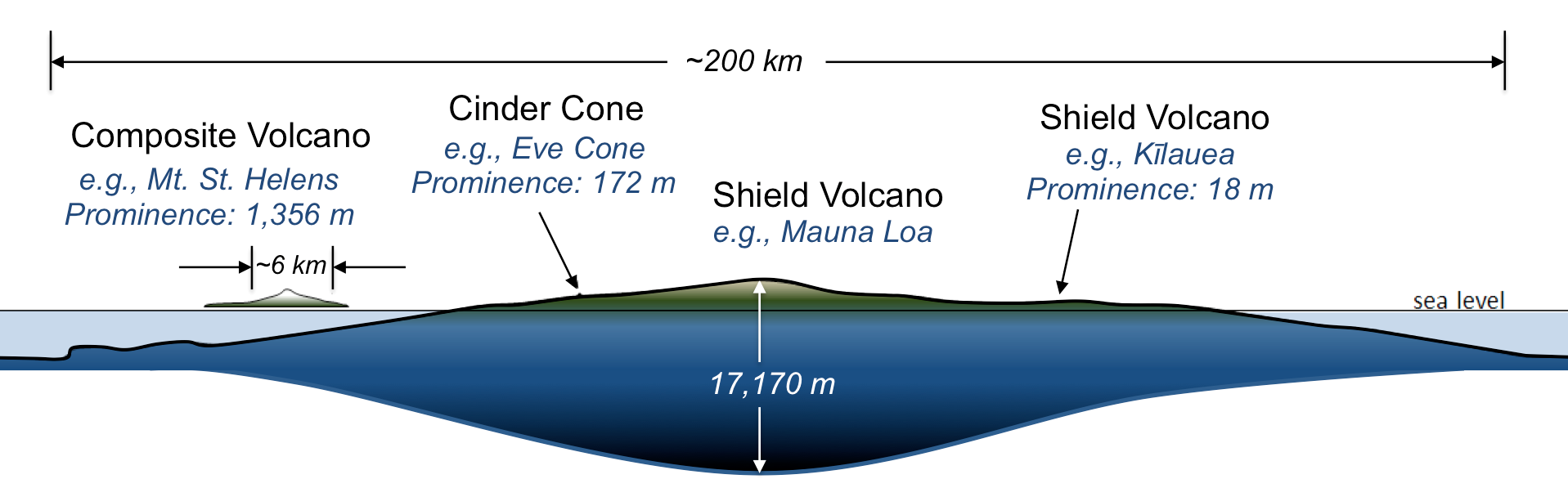
Cone-shaped mountain SHIELD VOLCANOES. Huge holes CINDER CONE VOLCANOES. Composite volcanoes sometimes called stratovolcanoes are typically deep-sided symmetrical cones of large dimension built of alternating layers of lava flows volcanic ash cinders blocks and bombs and may rise as much as 8000 ft above their bases.
The volcanoes of southwestern Alaska and the Aleutian Islands. Reverse fault raised block of rock between two normal faults 4. Which of the following best describes seamounts islands of the deep ocean basins.
This cloud condensed and eventually collapsed from its own gravitational pull. Massive gently sloping volcanoes built of successive basaltic lava flows. Which best describes the way composite volcanoes are built up.
Cinder cone volcano an underwater volcano that never surfaces 6. Sometimes the summit crater collapses to form a caldera. Composite volcanoes are made of cinders ash and lava.
There is an area of low topography southwest of Yellowstone. Cinder cone volcano an underwater volcano that never surfaces 6. Steep cone shaped-hill COMPOSITE VOLCANOES.
This explanation best describes _____. Strike-slip fault feature formed from rock and ash 5. Cinders and ash pile on top of each other lava flows on top of the ash where it cools and hardens and then the process repeats.
Composite volcano break in rock formed from colliding plates. There are shield volcanoes like the Hawaiian Islands which are built up from mostly repeated episodes of lava flows. Because they are built of layers of viscous material rather than fluid lava composite volcanoes tend to form tall peaks rather than rounded cones.
Which best describes the shape of classic composite cones. Composite volcano break in rock formed from colliding. Some of the most beautiful mountains in the world are composite volcanoes including Mount Fuji in Japan.
Monocline very large bowl-like feature formed from an explosive eruption 2. Some volcanoes such as stratovolcano or composite volcanoes are built up from multiple explosive eruptions of lava flows ash and other pyroclastic debris. Small basaltic cones built during one short eruptive episode.
The heat and pressure built up forming a protostar. Reverse fault raised block of rock between two normal faults 4. Large areas of flat land CCCSL What is the term for the huge holes left by the collapse of.
A __________ volcano is a very large gently sloping mound composed mainly of basaltic lava flows. Monocline very large bowl-like feature formed from an explosive eruption 2. Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount Shasta in California are examples of composite volcanoes.
Due to its viscous lava a composite volcano tends to form tall peaks rather than rounded cones. Massive gently sloping volcanoes built of successive basaltic lava flows. This stickiness plugs up the volcano causing pressure to build-up.
Shield volcanoes are volcanoes shaped like a bowl or shield in the middle with long gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows. Dike simple fold in rock layers 3.
11 3 Types Of Volcanoes Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition

11 3 Types Of Volcanoes Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition
11 3 Types Of Volcanoes Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition
No comments for "Which Best Describes the Way Composite Volcanoes Are Built Up"
Post a Comment